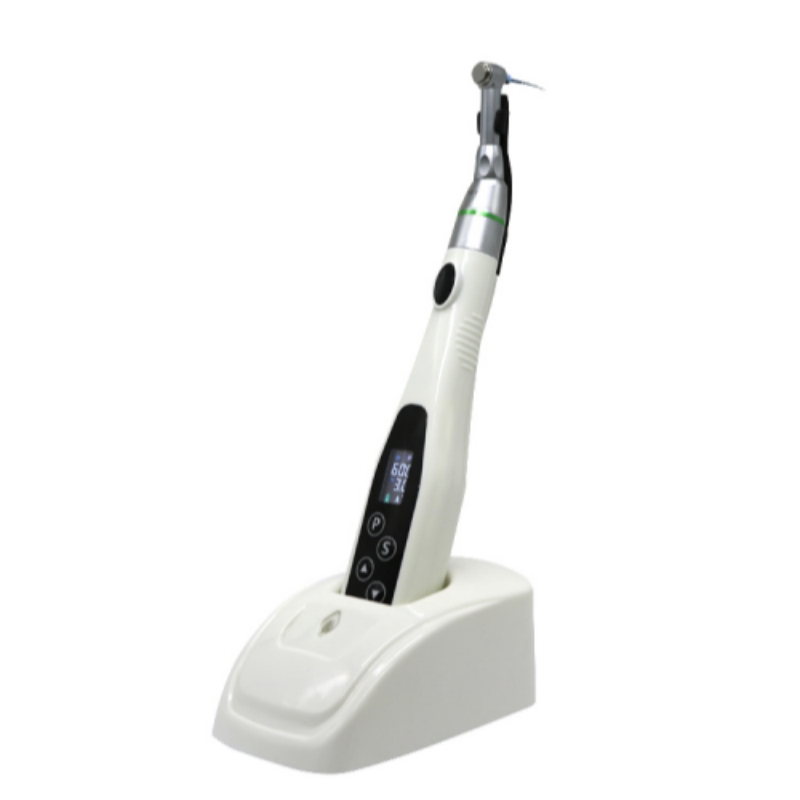
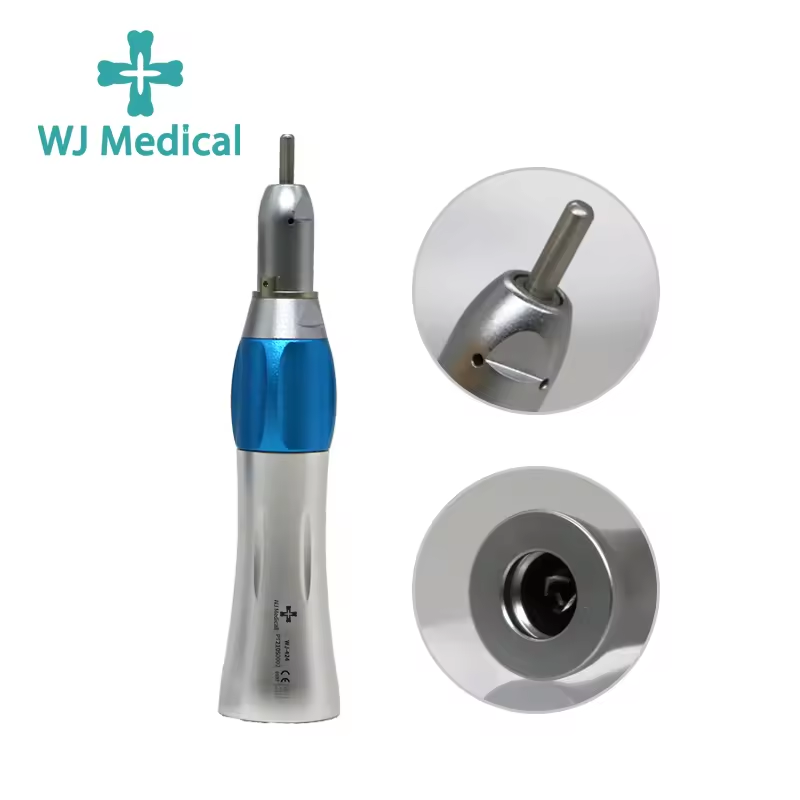
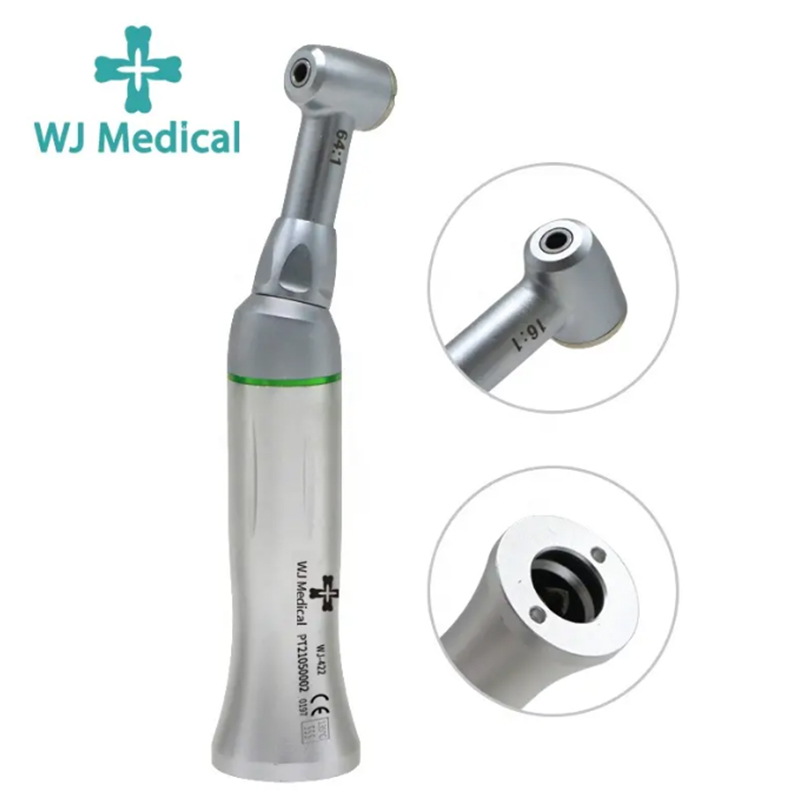
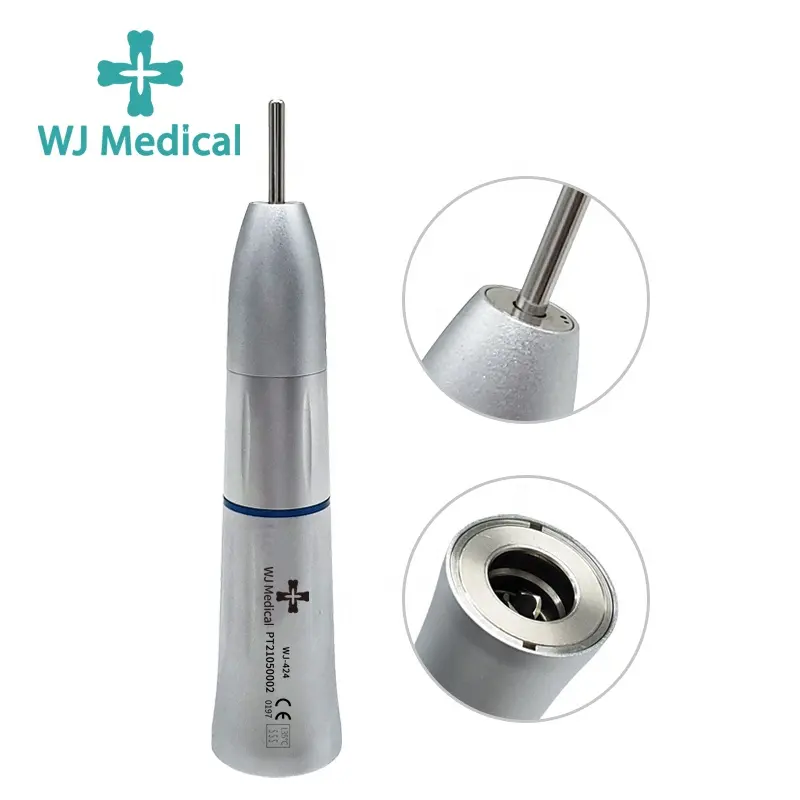
When is a dental endomotor used?
A dental endomotor, also known as an endodontic motor, is used primarily in endodontics, specifically during root canal treatment. Here are the key instances and considerations for its use:
During Root Canal Procedures
Shaping the Canal: The endomotor is utilized to shape the root canal by using rotary instruments at precise speeds and torques. This helps to remove infected or damaged pulp tissue and prepare the canal for filling.
Filing and Cleaning: With the help of endomotor-driven instruments, dentists can efficiently file and clean the root canal walls, ensuring that all debris and bacteria are removed.
Advantages of Using a Dental Endomotor
Precision and Control: The endomotor allows for greater precision and control during the procedure, reducing the risk of over-instrumentation or canal perforation.
Efficiency: It significantly speeds up the root canal treatment process, making it more efficient for both the dentist and the patient.
Comfort: By reducing the physical effort required to perform the procedure, the endomotor can make the treatment more comfortable for the patient.
Considerations for Use
Training and Expertise: The use of a dental endomotor requires specific training and expertise. Dentists should be familiar with the instrument's operation and the types of instruments compatible with it.
Patient Suitability: While the endomotor is generally suitable for most patients requiring root canal treatment, individual factors such as canal anatomy and severity of infection may influence its use.
Instrument Compatibility: Ensure that the endomotor is compatible with the rotary instruments being used. Different instruments may require different torque and speed settings.
Conclusion
In summary, a dental endomotor is an essential tool in endodontics, particularly during root canal treatment. It offers precision, control, and efficiency, making the treatment process more comfortable and effective for patients. However, its use requires specific training and expertise, and individual patient factors should be considered when determining its suitability.